Today's Saturday • 8 mins read
— By Dr. Sandip Roy.
Life is full of daily battles for grown-ups with ADHD, especially women. They often struggle in every imaginable domain: biological, interpersonal, social, and professional.
Sadly, many suffer in silence because they don’t realize they have the condition for fear of social stigma.
Early diagnosis of ADHD allows for earlier treatment and greater relief from its symptoms. Those who got themselves diagnosed and are undergoing some form of therapy for it often reframe ADHD as their superpower.
This study followed adolescents with childhood-onset ADHD for 8 years. They found:
- 30% achieved stable full remission
- 40% had some symptom remission
- 15% had unstable symptoms
The best part: Once an ADHD’er gets diagnosed and starts treatment, their world opens up in a way that many describe as “magical.” They become excellent at organizing their days, actively listening to others, and stop putting things off.
If you’re a grown-up (especially a woman) with ADHD, there is hope that you might outgrow your condition and live a happier life.
How To Take Charge of Your ADHD As A Woman
The 4 steps are:
- be open to considering that your symptoms might be ADHD
- take an online ADHD test (but do not yet mark yourself as ADHD)
- consult a mental health expert to get yourself diagnosed with ADHD
- if you have ADHD, adhere to the treatment plan and follow up as advised.
Women With ADHD: The Hidden Struggle
Many think ADHD affects all genders in the same way. However, research shows that girls and women with ADHD face two unique challenges: social expectations and clinical oversights.
Social Expectations From Women
Society expects girls and women to be calm, focused, and socially skilled, things that are the opposite of ADHD symptoms.
Academically successful girls may develop perfectionist tendencies to cope with their ADHD challenges. Trying to meet these lofty expectations and overcompensating gets exhausting for them.
When they inevitably fall short, their feelings of inadequacy lead to burnout, anxiety, and shame.
Yet, they hesitate to ask for help. Instead, they put up a face of having it all together to hide their self-doubts and struggles. Eventually, they settle for suffering their ADHD symptoms in silence.

What Makes ADHD Different for Girls?
- ADHD was first defined by studying hyperactive boys, so the criteria did not consider how it presents differently in girls.
- Girls tend to have the inattentive type of ADHD rather than the hyperactive type seen in boys.
- Instead of disruptive behavior, girls with ADHD often internalize their struggles with low self-esteem, anxiety, and negative self-talk.
Hormones and ADHD
- Hormone fluctuations from puberty, menstrual cycles, and menopause can worsen ADHD symptoms in women.
- PMS (premenstrual symptoms) can make women have more irritability, mood swings, poor sleep, and concentration issues.
- Many women are misdiagnosed with PMS or PMDD instead of having their ADHD identified.
Complicating Factors in Women with ADHD
- Women with ADHD often develop related issues like anxiety, depression, eating disorders and substance abuse.
- These get diagnosed first, masking the underlying ADHD.
- Trauma, abuse, and sensory processing issues can further complicate the clinical picture.
Hidden Risks
- Dismissed as “scatter-brained,” many women with ADHD go undiagnosed and untreated.
- This raises their risk for accidental injuries, self-harm, relationship problems, and earlier death.
- But an ADHD diagnosis can provide self-compassion and strategies to improve daily functioning.
Clinicians must recognize ADHD’s unique presentation in women and probe beyond stereotypical male symptoms.

Handling The 3 Challenges of Your ADHD
Awareness, diagnosis, and treatment are the three main areas to handle your ADHD.
Awareness
1. What Causes ADHD
Researchers think ADHD is likely caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetics plays a major role, as ADHD tends to run in families. Children born to mothers with anxiety disorders also have an elevated risk.
- Brain injuries, particularly to the frontal lobe, which controls emotions and impulses, can trigger ADHD symptoms.
- Substance abuse by pregnant mothers has been linked to causing ADHD in their children as well.
- Finally, certain environmental toxins like lead exposure, even at low levels, may dramatically increase the risk of developing ADHD (Donzelli et al., 2019).
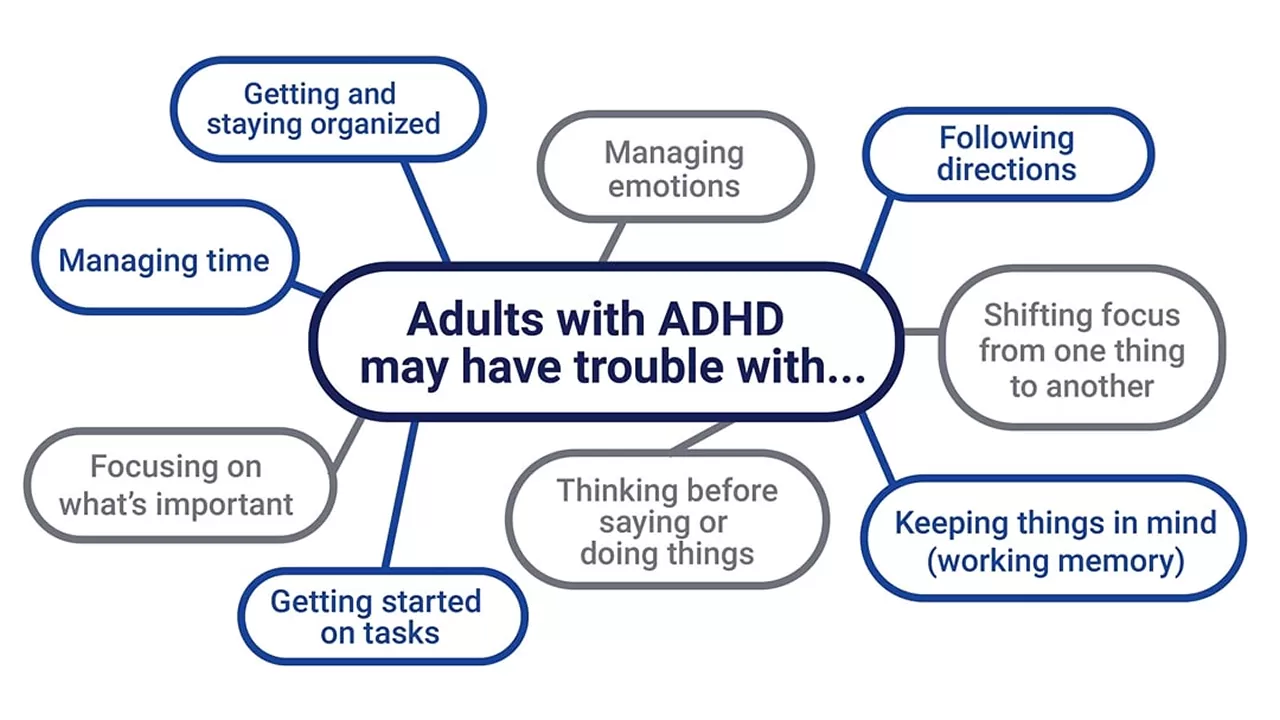
2. Problems Faced By ADHD’ers
- Mostly anxious, disorganized, and easily irritated.
- Show sudden outbursts and irrational shifts in behavior and mood.
- Most grown-ups with ADHD feel restless, forget details, and have shifty attention.
- They often get frustrated and stuck with feelings of emptiness and hopelessness.
- They cannot easily switch focus from one task to another or control their emotional reactions.
- Act on their impulses without thinking. Get obsessed with a particular thing for days, weeks, or months.

Did you know about the dark side of ADHD?
Diagnosis
ADHD (Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects 2.5% of grown-ups worldwide and 4.4% of US citizens (Faraone et al., 2015). There are 3 types of ADHD:
- Primary Inattentive, who struggle to maintain attention (common in girls)
- Primary Hyperactive-Impulsive, who have hyperactivity and impulsivity (common in boys)
- Combined, with signs of both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity (commonest overall)
1. Symptoms of ADHD In Grown-ups
Three hallmark symptoms of ADHD are inattention (inability to keep focus), hyperactivity (excessive movements that do not fit the setting), and impulsivity (hasty acts done at the moment without thought; experts call it reduced executive functioning).
Inattention Symptoms:
Inattention: a problem in paying attention to the tasks at hand.
- Displays poor listening skills
- Loses and/or misplaces items needed to complete activities or tasks
- Sidetracked by external or unimportant stimuli
- Forgets daily activities
- Diminished attention span
- Lacks the ability to complete work and other assignments, or to follow instructions
- Avoids or is disinclined to begin work or activities requiring concentration
- Fails to focus on details and/or makes thoughtless mistakes in work or assignments
Hyperactivity Symptoms:
Hyperactivity: an issue with possessing too much energy and aggressiveness when doing your daily activities.
- Overly talkative
- Marked restlessness that is difficult to control
- Incapable of staying calmly seated in a meeting or class
- Squirms when seated for long or fidgets with feet/hands
- Appears to be driven by “a motor” or is often “on the go”
- Lacks the ability to play and engage in leisure activities quietly
Impulsivity Symptoms:
Impulsivity: the inability to control your emotions, especially when in public spaces.
- Has difficulty waiting for their turn
- Impulsively blurts out answers before questions are completed
- Interrupts or intrudes into the conversations and activities of others
Impulsivity and hyperactivity are both risky conditions that can escalate to other harmful behaviors, such as drug and substance abuse and alcohol addiction.
2. How to diagnose if you have ADHD
- An online self-test may indicate you may have ADHD, but it cannot prove it.
- Get an in-person expert consultation to screen and test for ADHD, and receive a proper diagnosis if you have the condition or not.
Online Self-Tests For ADHD
- Psycom’s 3-minute Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder self-test to see if you may benefit from diagnosis and treatment. Link: ADHD Test (Self-Assessment)
- ADHD checklist to find out a better insight into your condition before you consult your healthcare provider for ADHD. Link: Is it or isn’t it ADHD?
- The World Health Organization’s ADHD Self-Report Scales (ASRS) Screener can help you recognize the signs and symptoms of ADHD. The ASRS comprises six questions that are ranked on a scale of 0 to 4. If you have at least four of these six symptoms significantly, you may have ADHD and should seek a formal diagnosis.
- Researchers from the University of California have created a smartphone app that scans the size of pupils to screen for ADHD. They published their findings, saying it can be a low-cost and high-accuracy way to help get more people screened for ADHD.
3. Diagnostic Criteria For ADHD As Per DSM-5
Mental health specialists and clinicians use the standardized Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders criteria to diagnose someone with ADHD:
A person aged ≥ 17 years with at least 5 inattentive and/or 5 hyperactive/impulsive symptoms for ≥ 6 months in ≥ 2 settings (e.g., workplace, home, church). The symptoms must be severe enough to interfere with their social, academic, or occupational activities.
Treatment
Get a referral from someone who’s had great results with their therapist/doctor.
Medicines
Stimulant medications help improve focus and reduce impulsivity. Antidepressants are also prescribed. Five medicines licensed for the treatment of ADHD are:
- methylphenidate (Focalin, Concerta)
- lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse)
- dexamfetamine (Adderall)
- atomoxetine (Strattera)
- guanfacine (Tenex)
Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common non-drug approach. It provides personalized strategies to change behaviors and improve self-management.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Get enough sleep
- Avoid triggering situations
- Maintain personal boundaries
Further Reading: Taking Charge of ADHD: Proven Strategies to Succeed at Work, at Home, and in Relationships by Russell A. Barkley and Christine M. Benton.
Final Words
A 2025 study found that people with ADHD have shorter lives. Women diagnosed with attention-deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) die 8.64 years earlier than those without the condition. Similarly, men with ADHD die 6.78 years earlier on average than those without.
ADHD is not a sentence. It is a treatable condition that you can learn to take charge of.
Women with ADHD, please seek diagnosis and treatment as early as you can. Therapy can help you enjoy a normal life and flourish at work.
√ Also Read: What Is Overthinking Or Rumination (Psychology Made Easy)
√ Please spread the word if you found this helpful.
» You deserve happiness! Choosing therapy could be your best decision.
...
• Disclosure: Buying via our links earns us a small commission.
