Today's Thursday • 7 mins read
Some people have a strong need to impress others or feel important. This can be a sign of narcissism. This need can be healthy or harmful, depending on how strong it is:
- “Positive narcissists” can get along well in society. They usually don’t hurt other people.
- Pathological narcissists show extreme behaviors. They can hurt others to make themselves feel better or assert their entitlement and importance.
The most serious form is the clinically diagnosed form of pathological narcissism, called Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD).
Narcissism looks different in boys and girls. Male narcissists grow up to be different from female narcissists. This difference could affect how we understand, diagnose, and treat it.
Are the men more narcissistic, really?
Research suggests narcissism is more common in men than in women.
- The Cleveland Clinic says 50–75% of NPD cases affect men.
- A 2008 study found that men have a 7.7% lifetime chance of getting NPD, whereas women have a 4.8% chance, among the general population.
- Emily Grijalva condensed 31 years of narcissism research, involving 475,000 people, to conclude that men are up to 75% more likely to be diagnosed with narcissistic personality disorder (NPD), and report significantly higher scores on the narcissism scale compared to women.
Are men truly more narcissistic, or are many women with narcissism left untreated or misdiagnosed?
Men Narcissists vs. Women Narcissists
Male and female narcissists act in different ways. Studies show that more men have NPD than women. About 8 out of 100 men will have NPD in their lifetime. Only 5 out of 100 women will have it.
Overt vs. Covert Narcissism
- Men often show narcissism in more grandiose ways. They tend to act loud, proud, bossy, and demanding of special treatment.
- Women may show narcissism in more covert, vulnerable ways. They might use body language, eye contact, tearfulness, or vocal tone changes to control others. They also tend to feel inadequate more often.
Specific Traits
- Men score slightly higher than women in leadership/authority and exploitative/entitlement aspects of narcissism.
- Men tend to make more extreme choices and decisions. These choices can be positive or negative.
Societal Expectations
- Social pressure affects how narcissism shows up. Men feel pressured to be successful, driven, and strong. Women feel pressured to look good and take care of others.

Relationships: Male vs. Female Narcissists
Narcissism affects relationships in different ways for men and women.
How They Act in Relationships
- Narcissistic men may boss their partners around or ignore their feelings or opinions.
- Women narcissists may get overly enmeshed with their partners. This means they see their partner as part of themselves, not as a separate person.
- Both male and female narcissists lack emotional empathy. Both try to control their partners. Both also think they deserve more special treatment in the relationship.
Cheating
- Narcissistic men cheat more often. It may be because they feel more entitled and have less empathy for their partners.
- Narcissistic women, especially those who use their looks to manipulate people, may also cheat. They do this to get attention and validation. Female narcissistic cheating patterns are interesting.
How Society Views Them
- Women are conditioned to look good, as society puts a high value on their appearances. So, women narcissists may get overlooked when they dress up to look attractive.
Overt vs. Covert Narcissism
Men usually show their narcissism openly. They may act arrogantly, bossy, or demanding without feeling inhibited.
Women tend to hide their narcissism better. They may in covert and vulnerable ways, as emotional blackmail and playing the victim.
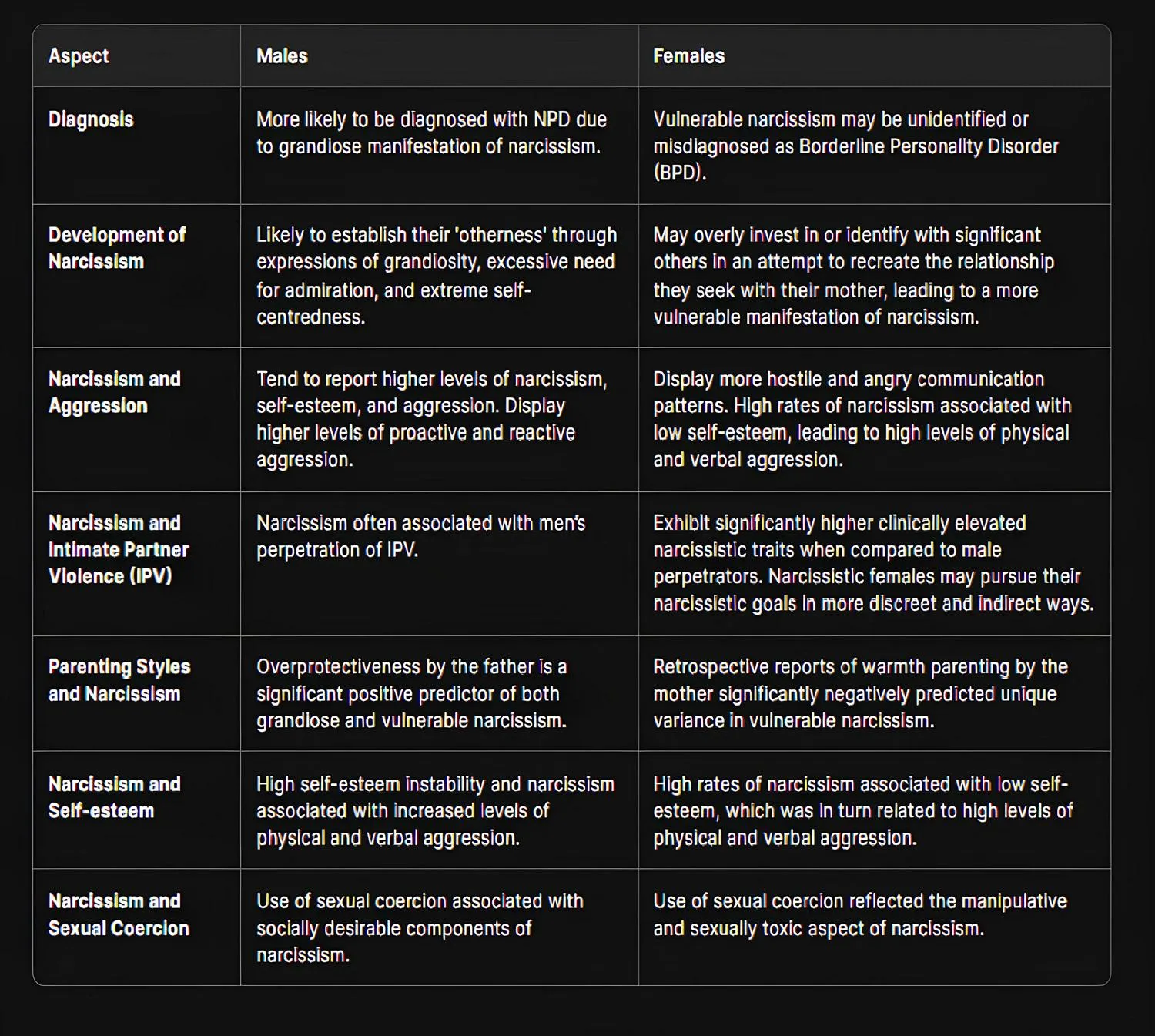
See this table of differences between male and female narcissists:
| Features | Male Narcissists | Female Narcissists |
|---|---|---|
| Getting Diagnosed | Doctors are more likely to say men have NPD. This is because men show their narcissism more openly. | Doctors are less likely to say women have NPD. Instead, they might say women have BPD (Borderline Personality Disorder). |
| How It Starts | Men show they are special by acting loud and proud. They need lots of praise and lack empathy for others. | Women may focus too much on important people in their lives. They try to fix the relationship they wanted with their mother. |
| Aggression | Men with narcissism are more hurtful than women. They start fights and react aggressively to problems. Men also learn to be physically hurtful when they are angry. | Women with high narcissism tend to have low self-esteem. They talk in more hostile and angry ways. They can be hurtful with words and actions. Women learn to be verbally hurtful when they are angry. |
| Intimate Partner Abuse | Male narcissists are often hostile toward their romantic partners. | Female narcissists hurt their partners more than male ones do. But they do it in indirect ways that are harder to spot. |
| How Parents Affect Them (Parenting Styles) | Overprotectiveness by the father may lead to both grandiose and vulnerable narcissism later. | When mothers are cold and don’t care much, children may get vulnerable narcissism later. |
| Self-esteem | Narcissistic men with shaky self-esteem tend to hurt others more with both words and actions. They also exploit others more. | Narcissistic women think they deserve special treatment from their partners. They often use emotional manipulation. |
Grijalva & Newman (2015) found the mean difference in narcissism between men and women remains the same from childhood to adulthood. That is, male and female narcissists at various ages remain “similarly different.”
Social Conditioning of Men vs. Women Narcissists
Gender socialization means learning how to act as a man or a woman based on what family, peers, and culture teach. These forces can shape how narcissism shows up in men and women.
- Boys are pushed to be independent, controlling, and powerful. This can feed grandiose narcissism. They learn to show off their status, expect praise, and feel high entitlement.
- Girls are pushed to form close, emotionally dependent bonds with their mothers and to become an “ideal woman.” They often rely on their mother’s approval. If that approval is inconsistent, they may develop low self‑worth and become sensitive to criticism. Over time, this can lead to vulnerable narcissism. They feel insecure and emotionally unstable and seek constant reassurance.

Gender Bias In Narcissism Diagnosis
The DSM is the official guide clinicians use to diagnose mental disorders. But it gives more attention to grandiose narcissism, more common in men. And gives less space to vulnerable narcissism, which is more common in women.
Gender socialization and these DSM biases can shape how NPD gets diagnosed.
- Clinicians are more likely to diagnose men with NPD because grandiose traits, like showing off, seeking admiration, and feeling superior, are easier to spot.
- Women with vulnerable narcissism often have traits like insecurity, shame, mood swings, and a strong fear of rejection. These are more likely to be misdiagnosed, overlooked, or mistreated. Many women with vulnerable narcissism are treated as Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) instead of NPD.
- Find out the 20 Definite Signs of A Narcissist.
Male vs. Female Narcissists In Partner Abuse
Intimate Partner Abuse is physical, sexual, and psychological abuse toward an intimate partner. Green & Hart (2024) found that male and female narcissists show different forms of IPV:
- Hostile female narcissists show higher levels of narcissism than hostile male narcissists.
- Female narcissists are more often reported to exhibit physical hostile behavior like shoving, hitting, breaking things, and verbal put‑downs.
- Hostile female narcissists are more likely to have narcissistic mothers, while hostile male narcissists are more likely to have narcissistic fathers.
Final Words
We have learned a lot about narcissism, far beyond the Greek myth of Narcissus and Echo.
But we still don’t know enough about how men and women show narcissism differently. Current studies don’t focus enough on these differences.
√ Also Read: 20 Female Narcissist Cheating Patterns – The Typical Traits
√ Please spread the word if you found this helpful.
» You deserve happiness! Choosing therapy could be your best decision.
...
• Disclosure: Buying via our links earns us a small commission.

